Quelles dépendances maven inclure pour spring 3.0?
J'essaie de faire mon premier projet avec Spring 3.0 (et maven). J'ai utilisé Spring 2.5 (et les versions primer) dans certains projets. Néanmoins, je suis un peu confus, quels modules je dois définir comme dépendances dans mon pom.XML. Je veux juste utiliser les fonctions de conteneur de base (beans, core, context, el).
J'étais habitué à faire ceci:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring</artifactId>
<version>2.5.6</version>
</dependency>
Mais maintenant je suis un peu confus, car il n'y a plus de module spring complet pour la version 3.0. J'ai essayé ce qui suit mais il n'a pas fonctionné (certaines classes sont manquantes).
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-expression</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
Toute aide serait appréciée!
7 réponses
Il y avait un très bon post sur le Spring Blog de Keith Donald détaillant howto obtenir printemps 3 Aritfacts avec Maven , avec des commentaires détaillant quand vous auriez besoin de chacune des dépendances...
<!-- Shared version number properties -->
<properties>
<org.springframework.version>3.0.0.RELEASE</org.springframework.version>
</properties>
<!-- Core utilities used by other modules.
Define this if you use Spring Utility APIs
(org.springframework.core.*/org.springframework.util.*)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Expression Language (depends on spring-core)
Define this if you use Spring Expression APIs
(org.springframework.expression.*)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-expression</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Bean Factory and JavaBeans utilities (depends on spring-core)
Define this if you use Spring Bean APIs
(org.springframework.beans.*)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Aspect Oriented Programming (AOP) Framework
(depends on spring-core, spring-beans)
Define this if you use Spring AOP APIs
(org.springframework.aop.*)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Application Context
(depends on spring-core, spring-expression, spring-aop, spring-beans)
This is the central artifact for Spring's Dependency Injection Container
and is generally always defined-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Various Application Context utilities, including EhCache, JavaMail, Quartz,
and Freemarker integration
Define this if you need any of these integrations-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Transaction Management Abstraction
(depends on spring-core, spring-beans, spring-aop, spring-context)
Define this if you use Spring Transactions or DAO Exception Hierarchy
(org.springframework.transaction.*/org.springframework.dao.*)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JDBC Data Access Library
(depends on spring-core, spring-beans, spring-context, spring-tx)
Define this if you use Spring's JdbcTemplate API
(org.springframework.jdbc.*)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Object-to-Relation-Mapping (ORM) integration with Hibernate, JPA and iBatis.
(depends on spring-core, spring-beans, spring-context, spring-tx)
Define this if you need ORM (org.springframework.orm.*)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Object-to-XML Mapping (OXM) abstraction and integration with JAXB, JiBX,
Castor, XStream, and XML Beans.
(depends on spring-core, spring-beans, spring-context)
Define this if you need OXM (org.springframework.oxm.*)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-oxm</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Web application development utilities applicable to both Servlet and
Portlet Environments
(depends on spring-core, spring-beans, spring-context)
Define this if you use Spring MVC, or wish to use Struts, JSF, or another
web framework with Spring (org.springframework.web.*)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring MVC for Servlet Environments
(depends on spring-core, spring-beans, spring-context, spring-web)
Define this if you use Spring MVC with a Servlet Container such as
Apache Tomcat (org.springframework.web.servlet.*)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring MVC for Portlet Environments
(depends on spring-core, spring-beans, spring-context, spring-web)
Define this if you use Spring MVC with a Portlet Container
(org.springframework.web.portlet.*)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc-portlet</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Support for testing Spring applications with tools such as JUnit and TestNG
This artifact is generally always defined with a 'test' scope for the
integration testing framework and unit testing stubs-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
Spring (de nos jours) facilite l'ajout de Spring à un projet en utilisant une seule dépendance, par exemple
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>3.1.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
Cela résoudra à
[INFO] The following files have been resolved:
[INFO] aopalliance:aopalliance:jar:1.0:compile
[INFO] commons-logging:commons-logging:jar:1.1.1:compile
[INFO] org.springframework:spring-aop:jar:3.1.2.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] org.springframework:spring-asm:jar:3.1.2.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] org.springframework:spring-beans:jar:3.1.2.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] org.springframework:spring-context:jar:3.1.2.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] org.springframework:spring-core:jar:3.1.2.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] org.springframework:spring-expression:jar:3.1.2.RELEASE:compile
Jetez un oeil à la page Spring Framework documentation pour plus d'informations.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
Comme ces questions semblent encore avoir beaucoup de vues, il peut être utile de noter que pour Spring 4+, il est plus facile de commencer à utiliser Spring Boot et les POMs de démarrage Spring Boot.
En utilisant Spring Boot, il y a moins de dépendances à gérer (et donc moins de conflits), et la mise en place d'un contexte Spring fonctionnel et bien intégré est beaucoup plus facile. Je le recommande fortement.
Quelles classes manquent? Le nom de la classe lui-même devrait être un bon indice du module manquant.
Pour info, je sais qu'il est vraiment pratique d'inclure le pot Uber spring, mais cela pose vraiment des problèmes lors de l'intégration avec d'autres projets. L'un des avantages derrière le système de dépendance est qu'il résoudra les conflits de version entre les dépendances.
Si ma bibliothèque dépend de printemps-core 2.5 et vous pouvez compter sur ma bibliothèque et uber-printemps:3.0, vous avez maintenant 2 versions du printemps sur votre chemin de classe.
Vous pouvez contourner cela avec des exclusions, mais il est beaucoup plus facile de lister les dépendances correctement et de ne pas avoir à vous en soucier.
Vous pouvez essayer ceci
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>`
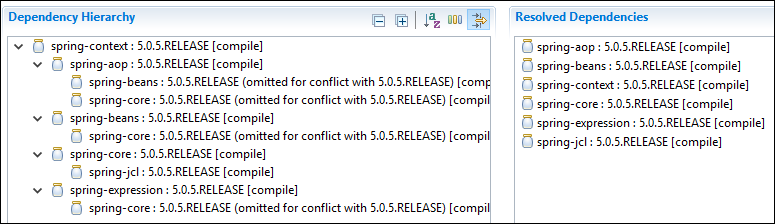
Vous pouvez ajouter printemps-contexte dépendance pour le printemps des bocaux. Vous obtiendrez les pots suivants avec elle.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
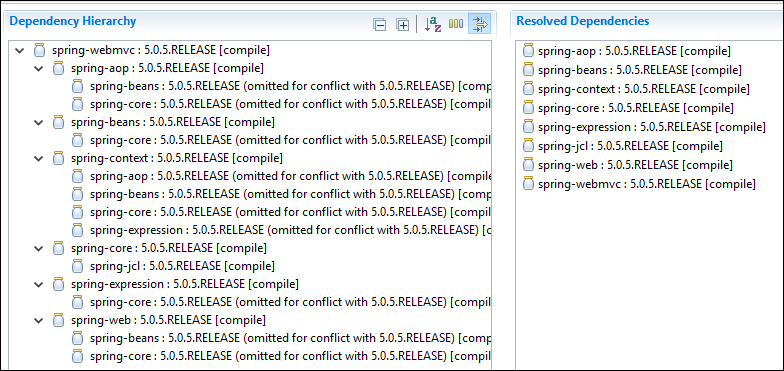
Si vous voulez également des composants web, vous pouvez utiliser la dépendancespring-webmvc .
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
Vous pouvez utiliser n'importe quelle version de ce que vous voulez. J'ai utilisé 5.0.5.Le COMMUNIQUÉ ici.