Envoyer une chaîne de caractères via Bluetooth depuis un PC en tant que client vers un mobile en tant que serveur
j'ai besoin d'aide en transférant une chaîne d'un PC vers un appareil mobile Android via Bluetooth. L'appareil mobile Android devrait agir comme un serveur et d'afficher la chaîne de message sur l'écran de l'appareil. Le PC qui est le client doit envoyer la chaîne à l'appareil mobile.
je veux que le serveur réagisse sur la chaîne extraite (transférée via Bluetooth). Cela signifie que d'un côté le serveur doit toujours écouter les nouvelles chaînes pour arriver, mais de l'autre side doit encore être capable de réagir sur ces messages (par exemple, naviguer d'un menu à l'autre).
j'ai essayé en utilisant BlueCove (2.1.1) comme BluetoothStack (pour lequel j'ajoute le jar de BlueCove comme Bibliothèque aux deux projets) en combinaison avec un exemple de communication serveur-client que j'ai trouvé ici .
Mises à jour:
mise à jour du code du serveur grâce à user_CC utilisation d'une connexion RFComm pour le serveur:
public class RFCommServer extends Thread{
//based on java.util.UUID
private static UUID MY_UUID = UUID.fromString("446118f0-8b1e-11e2-9e96-0800200c9a66");
// The local server socket
private BluetoothServerSocket mmServerSocket;
// based on android.bluetooth.BluetoothAdapter
private BluetoothAdapter mAdapter;
private BluetoothDevice remoteDevice;
private Activity activity;
public RFCommServer(Activity activity) {
this.activity = activity;
}
public void run() {
BluetoothSocket socket = null;
mAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
// Listen to the server socket if we're not connected
while (true) {
try {
// Create a new listening server socket
Log.d(this.getName(), ".....Initializing RFCOMM SERVER....");
// MY_UUID is the UUID you want to use for communication
mmServerSocket = mAdapter.listenUsingRfcommWithServiceRecord("MyService", MY_UUID);
//mmServerSocket = mAdapter.listenUsingInsecureRfcommWithServiceRecord(NAME, MY_UUID); // you can also try using In Secure connection...
// This is a blocking call and will only return on a
// successful connection or an exception
socket = mmServerSocket.accept();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
try {
Log.d(this.getName(), "Closing Server Socket.....");
mmServerSocket.close();
InputStream tmpIn = null;
OutputStream tmpOut = null;
// Get the BluetoothSocket input and output streams
tmpIn = socket.getInputStream();
tmpOut = socket.getOutputStream();
DataInputStream mmInStream = new DataInputStream(tmpIn);
DataOutputStream mmOutStream = new DataOutputStream(tmpOut);
// here you can use the Input Stream to take the string from the client whoever is connecting
//similarly use the output stream to send the data to the client
RelativeLayout layout = (RelativeLayout) activity.findViewById(R.id.relativeLayout_Layout);
TextView text = (TextView) layout.findViewById(R.id.textView_Text);
text.setText(mmInStream.toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
//catch your exception here
}
}
}
Code du client SPP de ici :
/**
* A simple SPP client that connects with an SPP server
*/
public class SampleSPPClient implements DiscoveryListener{
//object used for waiting
private static Object lock=new Object();
//vector containing the devices discovered
private static Vector vecDevices=new Vector();
private static String connectionURL=null;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SampleSPPClient client=new SampleSPPClient();
//display local device address and name
LocalDevice localDevice = LocalDevice.getLocalDevice();
System.out.println("Address: "+localDevice.getBluetoothAddress());
System.out.println("Name: "+localDevice.getFriendlyName());
//find devices
DiscoveryAgent agent = localDevice.getDiscoveryAgent();
System.out.println("Starting device inquiry...");
agent.startInquiry(DiscoveryAgent.GIAC, client);
try {
synchronized(lock){
lock.wait();
}
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Device Inquiry Completed. ");
//print all devices in vecDevices
int deviceCount=vecDevices.size();
if(deviceCount <= 0){
System.out.println("No Devices Found .");
System.exit(0);
}
else{
//print bluetooth device addresses and names in the format [ No. address (name) ]
System.out.println("Bluetooth Devices: ");
for (int i = 0; i <deviceCount; i++) {
RemoteDevice remoteDevice=(RemoteDevice)vecDevices.elementAt(i);
System.out.println((i+1)+". "+remoteDevice.getBluetoothAddress()+" ("+remoteDevice.getFriendlyName(true)+")");
}
}
System.out.print("Choose Device index: ");
BufferedReader bReader=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String chosenIndex=bReader.readLine();
int index=Integer.parseInt(chosenIndex.trim());
//check for spp service
RemoteDevice remoteDevice=(RemoteDevice)vecDevices.elementAt(index-1);
UUID[] uuidSet = new UUID[1];
uuidSet[0]=new UUID("446118f08b1e11e29e960800200c9a66", false);
System.out.println("nSearching for service...");
agent.searchServices(null,uuidSet,remoteDevice,client);
try {
synchronized(lock){
lock.wait();
}
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(connectionURL==null){
System.out.println("Device does not support Simple SPP Service.");
System.exit(0);
}
//connect to the server and send a line of text
StreamConnection streamConnection=(StreamConnection)Connector.open(connectionURL);
//send string
OutputStream outStream=streamConnection.openOutputStream();
PrintWriter pWriter=new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(outStream));
pWriter.write("Test String from SPP Clientrn");
pWriter.flush();
//read response
InputStream inStream=streamConnection.openInputStream();
BufferedReader bReader2=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inStream));
String lineRead=bReader2.readLine();
System.out.println(lineRead);
}//main
//methods of DiscoveryListener
public void deviceDiscovered(RemoteDevice btDevice, DeviceClass cod) {
//add the device to the vector
if(!vecDevices.contains(btDevice)){
vecDevices.addElement(btDevice);
}
}
//implement this method since services are not being discovered
public void servicesDiscovered(int transID, ServiceRecord[] servRecord) {
if(servRecord!=null && servRecord.length>0){
connectionURL=servRecord[0].getConnectionURL(0,false);
}
synchronized(lock){
lock.notify();
}
}
//implement this method since services are not being discovered
public void serviceSearchCompleted(int transID, int respCode) {
synchronized(lock){
lock.notify();
}
}
public void inquiryCompleted(int discType) {
synchronized(lock){
lock.notify();
}
}//end method
}
pour tester J'utilise un Nexus Galaxy (GT-I9250) avec la dernière API Android.
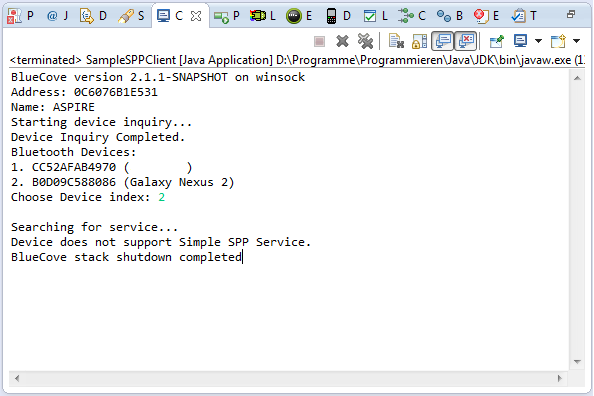
grâce à user_CC , le client et le serveur tournent maintenant sans exception. Mais malheureusement le client n'est pas capable de se connecter au serveur (voir la capture d'écran ci-dessous). C'est parce que l' connectionURL n'est jamais défini (il saute donc ici if(connectionURL==null) par défaut.
Comment puis-je changer le code client, de sorte que je puisse le connecter au serveur? J'ai besoin d'un bon connectionURL dans la ligne suivante:
StreamConnection streamConnection=(StreamConnection)Connector.open(connectionURL)
Jusqu'à présent j'ai seulement découvert que j'ai d'une manière ou d'une autre besoin d'obtenir le ServiceRecord , malheureusement ce n'est pas non plus décrit dans le code d'exemple de ici .
2 réponses
vous aurez besoin d'utiliser les API RFComm pour faire fonctionner la communication j'ai réussi à définir une classe qui est un Thread et qui agira comme un serveur et écoutera les connexions client. J'ai également fait quelques commentaires pour que vous les compreniez.
private class AcceptThread extends Thread {
// The local server socket
private BluetoothServerSocket mmServerSocket;
public AcceptThread() {
}
public void run() {
BluetoothSocket socket = null;
BluetoothAdapter mAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
// Listen to the server socket if we're not connected
while (true) {
try {
// Create a new listening server socket
Log.d(TAG, ".....Initializing RFCOMM SERVER....");
// MY_UUID is the UUID you want to use for communication
mmServerSocket = mAdapter.listenUsingRfcommWithServiceRecord(NAME, MY_UUID);
//mmServerSocket = mAdapter.listenUsingInsecureRfcommWithServiceRecord(NAME, MY_UUID); you can also try using In Secure connection...
// This is a blocking call and will only return on a
// successful connection or an exception
socket = mmServerSocket.accept();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
try {
Log.d(TAG, "Closing Server Socket.....";
mmServerSocket.close();
InputStream tmpIn = null;
OutputStream tmpOut = null;
// Get the BluetoothSocket input and output streams
tmpIn = socket.getInputStream();
tmpOut = socket.getOutputStream();
mmInStream = new DataInputStream(tmpIn);
mmOutStream = new DataOutputStream(tmpOut);
// here you can use the Input Stream to take the string from the client whoever is connecting
//similarly use the output stream to send the data to the client
} catch (Exception e) {
//catch your exception here
}
}
}
}
j'espère que cette aide
pour votre autre question:
déclarant javax.Bluetooth.UUID côté Client (PC) la classe UUID doit provenir de javax.Bluetooth.UUID
uuidSet2[0] = new UUID("446118f08b1e11e29e960800200c9a66", false);
déclarant java.util.UUID à Côté Serveur (Android)
UUID MY_UUID = UUID.fromString("446118f0-8b1e-11e2-9e96-0800200c9a66");
Je ne suis pas un développeur Java mais j'ai eu un problème similaire avec Mono pour Android (c#)
L'UUID pour les SPP doit être "00001101-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FB"
Il s'agit d'un UID bien connu pour identifier un adaptateur Bluetooth SPP.
dans mon code c qui ressemble à
private static UUID MY_UUID = UUID.FromString("00001101-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FB");
je suppose que vous pouvez mettre à jour votre code Java en quelque chose comme:
new UUID("00001101-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FB", true);
bien que je sois Je ne sais pas quels paramètres Cette fonction accepte, donc vous pourriez avoir à vérifier cela.
j'utilisais L'appareil Android comme client, mais les informations peuvent être utiles pour vous,
donc je vais inclure mon code c ici que j'ai traduit à l'origine à partir D'échantillons Java,
donc vous devriez être en mesure de le traduire en arrière:
btAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.DefaultAdapter;
btAdapter.CancelDiscovery(); //Always call CancelDiscovery before doing anything
remoteDevice = btAdapter.GetRemoteDevice(Settings["deviceaddress"].ToString());
socket = remoteDevice.CreateRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(MY_UUID);
socket.Connect();
en gros, J'obtiens l'adaptateur par défaut, j'annule toutes les opérations de découverte en cours et puis créer une socket pour l'autre périphérique. Dans votre cas, vous voudrez écouter au lieu de se connecter, mais juste pour votre information.
j'espère que cela aidera, désolé Je ne pouvais pas vous donner plus D'informations spécifiques à Java.
'mise à Jour:' Viens de trouver un petit échantillon en Java qui suit plus ou moins la même méthode comme ce que j'utilise: problèmes avec connexion bluetooth SPP dans android?