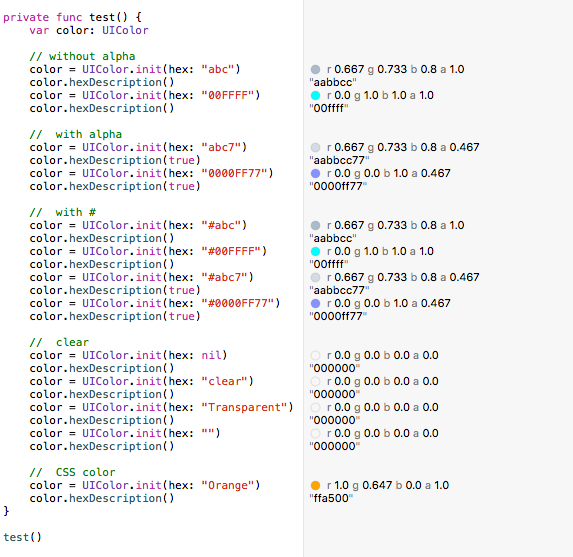
Comment utiliser les valeurs de couleurs hex
j'essaie d'utiliser les valeurs de couleur hexadécimales dans Swift, au lieu des quelques valeurs standards que UIColor vous permet d'utiliser, mais je n'ai aucune idée de comment le faire.
exemple: comment utiliser #ffffff comme couleur?
30 réponses
#ffffff sont en fait 3 composants de couleur en notation hexadécimale - rouge ff , Vert ff et bleu ff . Vous pouvez écrire la notation hexadécimale dans Swift en utilisant le préfixe 0x , E. g 0xFF
pour simplifier la conversion, créons un initialiseur qui prend des valeurs entières (0-255):
extension UIColor {
convenience init(red: Int, green: Int, blue: Int) {
assert(red >= 0 && red <= 255, "Invalid red component")
assert(green >= 0 && green <= 255, "Invalid green component")
assert(blue >= 0 && blue <= 255, "Invalid blue component")
self.init(red: CGFloat(red) / 255.0, green: CGFloat(green) / 255.0, blue: CGFloat(blue) / 255.0, alpha: 1.0)
}
convenience init(rgb: Int) {
self.init(
red: (rgb >> 16) & 0xFF,
green: (rgb >> 8) & 0xFF,
blue: rgb & 0xFF
)
}
}
Utilisation:
let color = UIColor(red: 0xFF, green: 0xFF, blue: 0xFF)
let color2 = UIColor(rgb: 0xFFFFFF)
comment obtenir alpha?
selon votre cas d'utilisation, vous pouvez simplement utiliser la méthode native UIColor.withAlphaComponent , par exemple
let semitransparentBlack = UIColor(rgb: 0x000000).withAlphaComponent(0.5)
ou vous pouvez ajouter un paramètre supplémentaire (optionnel) aux méthodes ci-dessus:
convenience init(red: Int, green: Int, blue: Int, a: CGFloat = 1.0) {
self.init(
red: CGFloat(red) / 255.0,
green: CGFloat(green) / 255.0,
blue: CGFloat(blue) / 255.0,
alpha: a
)
}
convenience init(rgb: Int, a: CGFloat = 1.0) {
self.init(
red: (rgb >> 16) & 0xFF,
green: (rgb >> 8) & 0xFF,
blue: rgb & 0xFF,
a: a
)
}
(nous ne pouvons pas nommer le paramètre alpha à cause d'une collision de nom avec l'initialiseur existant).
appelé comme:
let color = UIColor(red: 0xFF, green: 0xFF, blue: 0xFF, a: 0.5)
let color2 = UIColor(rgb: 0xFFFFFF, a: 0.5)
pour obtenir l'alpha comme un entier 0-255, nous pouvons
convenience init(red: Int, green: Int, blue: Int, a: Int = 0xFF) {
self.init(
red: CGFloat(red) / 255.0,
green: CGFloat(green) / 255.0,
blue: CGFloat(blue) / 255.0,
alpha: CGFloat(a) / 255.0
)
}
// let's suppose alpha is the first component (ARGB)
convenience init(argb: Int) {
self.init(
red: (argb >> 16) & 0xFF,
green: (argb >> 8) & 0xFF,
blue: argb & 0xFF,
a: (argb >> 24) & 0xFF
)
}
appelé
let color = UIColor(red: 0xFF, green: 0xFF, blue: 0xFF, a: 0xFF)
let color2 = UIColor(argb: 0xFFFFFFFF)
, Ou une combinaison des méthodes précédentes. Il n'est absolument pas nécessaire d'utiliser des cordes.
c'est une fonction qui prend une chaîne hex et renvoie un UIColor.
(vous pouvez entrer des chaînes hex avec l'un ou l'autre format: #ffffff ou ffffff )
Utilisation:
var color1 = hexStringToUIColor("#d3d3d3")
Swift 4:
func hexStringToUIColor (hex:String) -> UIColor {
var cString:String = hex.trimmingCharacters(in: .whitespacesAndNewlines).uppercased()
if (cString.hasPrefix("#")) {
cString.remove(at: cString.startIndex)
}
if ((cString.count) != 6) {
return UIColor.gray
}
var rgbValue:UInt32 = 0
Scanner(string: cString).scanHexInt32(&rgbValue)
return UIColor(
red: CGFloat((rgbValue & 0xFF0000) >> 16) / 255.0,
green: CGFloat((rgbValue & 0x00FF00) >> 8) / 255.0,
blue: CGFloat(rgbValue & 0x0000FF) / 255.0,
alpha: CGFloat(1.0)
)
}
Swift 3:
func hexStringToUIColor (hex:String) -> UIColor {
var cString:String = hex.trimmingCharacters(in: .whitespacesAndNewlines).uppercased()
if (cString.hasPrefix("#")) {
cString.remove(at: cString.startIndex)
}
if ((cString.characters.count) != 6) {
return UIColor.gray
}
var rgbValue:UInt32 = 0
Scanner(string: cString).scanHexInt32(&rgbValue)
return UIColor(
red: CGFloat((rgbValue & 0xFF0000) >> 16) / 255.0,
green: CGFloat((rgbValue & 0x00FF00) >> 8) / 255.0,
blue: CGFloat(rgbValue & 0x0000FF) / 255.0,
alpha: CGFloat(1.0)
)
}
Swift 2:
func hexStringToUIColor (hex:String) -> UIColor {
var cString:String = hex.stringByTrimmingCharactersInSet(NSCharacterSet.whitespaceAndNewlineCharacterSet() as NSCharacterSet).uppercaseString
if (cString.hasPrefix("#")) {
cString = cString.substringFromIndex(cString.startIndex.advancedBy(1))
}
if ((cString.characters.count) != 6) {
return UIColor.grayColor()
}
var rgbValue:UInt32 = 0
NSScanner(string: cString).scanHexInt(&rgbValue)
return UIColor(
red: CGFloat((rgbValue & 0xFF0000) >> 16) / 255.0,
green: CGFloat((rgbValue & 0x00FF00) >> 8) / 255.0,
blue: CGFloat(rgbValue & 0x0000FF) / 255.0,
alpha: CGFloat(1.0)
)
}
Source: arshad / gist:de147c42d7b3063ef7bc
Edit: mise à Jour du code. Merci, Hlung, jaytrixz, et Ahmad F!
Swift 4 UIColor extension:
extension UIColor {
convenience init(hexString: String) {
let hex = hexString.trimmingCharacters(in: CharacterSet.alphanumerics.inverted)
var int = UInt32()
Scanner(string: hex).scanHexInt32(&int)
let a, r, g, b: UInt32
switch hex.count {
case 3: // RGB (12-bit)
(a, r, g, b) = (255, (int >> 8) * 17, (int >> 4 & 0xF) * 17, (int & 0xF) * 17)
case 6: // RGB (24-bit)
(a, r, g, b) = (255, int >> 16, int >> 8 & 0xFF, int & 0xFF)
case 8: // ARGB (32-bit)
(a, r, g, b) = (int >> 24, int >> 16 & 0xFF, int >> 8 & 0xFF, int & 0xFF)
default:
(a, r, g, b) = (255, 0, 0, 0)
}
self.init(red: CGFloat(r) / 255, green: CGFloat(g) / 255, blue: CGFloat(b) / 255, alpha: CGFloat(a) / 255)
}
}
Utilisation :
let darkGrey = UIColor(hexString: "#757575")
Swift 2.x version:
extension UIColor {
convenience init(hexString: String) {
let hex = hexString.stringByTrimmingCharactersInSet(NSCharacterSet.alphanumericCharacterSet().invertedSet)
var int = UInt32()
NSScanner(string: hex).scanHexInt(&int)
let a, r, g, b: UInt32
switch hex.characters.count {
case 3: // RGB (12-bit)
(a, r, g, b) = (255, (int >> 8) * 17, (int >> 4 & 0xF) * 17, (int & 0xF) * 17)
case 6: // RGB (24-bit)
(a, r, g, b) = (255, int >> 16, int >> 8 & 0xFF, int & 0xFF)
case 8: // ARGB (32-bit)
(a, r, g, b) = (int >> 24, int >> 16 & 0xFF, int >> 8 & 0xFF, int & 0xFF)
default:
(a, r, g, b) = (255, 0, 0, 0)
}
self.init(red: CGFloat(r) / 255, green: CGFloat(g) / 255, blue: CGFloat(b) / 255, alpha: CGFloat(a) / 255)
}
}
UIColor :
extension UIColor {
convenience init(hex: Int) {
let components = (
R: CGFloat((hex >> 16) & 0xff) / 255,
G: CGFloat((hex >> 08) & 0xff) / 255,
B: CGFloat((hex >> 00) & 0xff) / 255
)
self.init(red: components.R, green: components.G, blue: components.B, alpha: 1)
}
}
CGColor :
extension CGColor {
class func colorWithHex(hex: Int) -> CGColorRef {
return UIColor(hex: hex).CGColor
}
}
l'Utilisation de la
let purple = UIColor(hex: 0xAB47BC)
avec Swift 2.0 et Xcode 7.0.1 vous pouvez créer cette fonction:
// Creates a UIColor from a Hex string.
func colorWithHexString (hex:String) -> UIColor {
var cString:String = hex.stringByTrimmingCharactersInSet(NSCharacterSet.whitespaceAndNewlineCharacterSet()).uppercaseString
if (cString.hasPrefix("#")) {
cString = (cString as NSString).substringFromIndex(1)
}
if (cString.characters.count != 6) {
return UIColor.grayColor()
}
let rString = (cString as NSString).substringToIndex(2)
let gString = ((cString as NSString).substringFromIndex(2) as NSString).substringToIndex(2)
let bString = ((cString as NSString).substringFromIndex(4) as NSString).substringToIndex(2)
var r:CUnsignedInt = 0, g:CUnsignedInt = 0, b:CUnsignedInt = 0;
NSScanner(string: rString).scanHexInt(&r)
NSScanner(string: gString).scanHexInt(&g)
NSScanner(string: bString).scanHexInt(&b)
return UIColor(red: CGFloat(r) / 255.0, green: CGFloat(g) / 255.0, blue: CGFloat(b) / 255.0, alpha: CGFloat(1))
}
et puis l'utiliser de cette façon:
let color1 = colorWithHexString("#1F437C")
Mise À Jour Pour Swift 4
func colorWithHexString (hex:String) -> UIColor {
var cString = hex.trimmingCharacters(in: CharacterSet.whitespacesAndNewlines).uppercased()
if (cString.hasPrefix("#")) {
cString = (cString as NSString).substring(from: 1)
}
if (cString.characters.count != 6) {
return UIColor.gray
}
let rString = (cString as NSString).substring(to: 2)
let gString = ((cString as NSString).substring(from: 2) as NSString).substring(to: 2)
let bString = ((cString as NSString).substring(from: 4) as NSString).substring(to: 2)
var r:CUnsignedInt = 0, g:CUnsignedInt = 0, b:CUnsignedInt = 0;
Scanner(string: rString).scanHexInt32(&r)
Scanner(string: gString).scanHexInt32(&g)
Scanner(string: bString).scanHexInt32(&b)
return UIColor(red: CGFloat(r) / 255.0, green: CGFloat(g) / 255.0, blue: CGFloat(b) / 255.0, alpha: CGFloat(1))
}
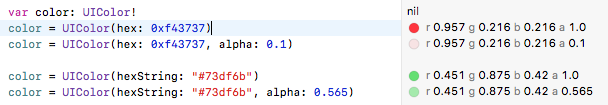
Swift 4 : combinant les réponses de Sulthan et Luca Torella :
extension UIColor {
convenience init(hexFromString:String, alpha:CGFloat = 1.0) {
var cString:String = hexFromString.trimmingCharacters(in: .whitespacesAndNewlines).uppercased()
var rgbValue:UInt32 = 10066329 //color #999999 if string has wrong format
if (cString.hasPrefix("#")) {
cString.remove(at: cString.startIndex)
}
if ((cString.count) == 6) {
Scanner(string: cString).scanHexInt32(&rgbValue)
}
self.init(
red: CGFloat((rgbValue & 0xFF0000) >> 16) / 255.0,
green: CGFloat((rgbValue & 0x00FF00) >> 8) / 255.0,
blue: CGFloat(rgbValue & 0x0000FF) / 255.0,
alpha: alpha
)
}
}
exemples d'utilisation:
let myColor = UIColor(hexFromString: "4F9BF5")
let myColor = UIColor(hexFromString: "#4F9BF5")
let myColor = UIColor(hexFromString: "#4F9BF5", alpha: 0.5)
Ce réponse montre comment le faire en Obj-C. Le pont est d'utiliser des
let rgbValue = 0xFFEEDD
let r = Float((rgbValue & 0xFF0000) >> 16)/255.0
let g = Float((rgbValue & 0xFF00) >> 8)/255.0
let b = Float((rgbValue & 0xFF))/255.0
self.backgroundColor = UIColor(red:r, green: g, blue: b, alpha: 1.0)
la façon la plus simple d'ajouter une couleur par programmation est d'utiliser ColorLiteral .
il suffit d'ajouter la propriété ColorLiteral comme indiqué dans l'exemple, Xcode vous demandera une liste complète de couleurs que vous pouvez choisir. L'avantage de le faire est un code plus petit, ajouter des valeurs HEX ou RGB . Vous obtiendrez également les couleurs utilisées récemment à partir du storyboard.
une autre méthode
Swift 3.0
écrire une extension pour UIColor
// To change the HexaDecimal value to Corresponding Color
extension UIColor
{
class func uicolorFromHex(_ rgbValue:UInt32, alpha : CGFloat)->UIColor
{
let red = CGFloat((rgbValue & 0xFF0000) >> 16) / 255.0
let green = CGFloat((rgbValue & 0xFF00) >> 8) / 255.0
let blue = CGFloat(rgbValue & 0xFF) / 255.0
return UIColor(red:red, green:green, blue:blue, alpha: alpha)
}
}
vous pouvez créer directement UIColor avec hex comme ceci
let carrot = UIColor.uicolorFromHex(0xe67e22, alpha: 1))
dernière Version de swift3
extension UIColor {
convenience init(hexString: String) {
let hex = hexString.trimmingCharacters(in: CharacterSet.alphanumerics.inverted)
var int = UInt32()
Scanner(string: hex).scanHexInt32(&int)
let a, r, g, b: UInt32
switch hex.characters.count {
case 3: // RGB (12-bit)
(a, r, g, b) = (255, (int >> 8) * 17, (int >> 4 & 0xF) * 17, (int & 0xF) * 17)
case 6: // RGB (24-bit)
(a, r, g, b) = (255, int >> 16, int >> 8 & 0xFF, int & 0xFF)
case 8: // ARGB (32-bit)
(a, r, g, b) = (int >> 24, int >> 16 & 0xFF, int >> 8 & 0xFF, int & 0xFF)
default:
(a, r, g, b) = (255, 0, 0, 0)
}
self.init(red: CGFloat(r) / 255, green: CGFloat(g) / 255, blue: CGFloat(b) / 255, alpha: CGFloat(a) / 255)
}
}
utiliser dans votre classe ou où jamais vous converti en hexcolor à uicolor comme de cette façon
let color1 = UIColor(hexString: "#FF323232")
mise à Jour sur 2018/06/14
l'échantillon doit fonctionner sur Swift2.2, Swift2.3, Swift3, Swift4:
public extension UIColor {
convenience init(hex: Int, alpha: Double = 1.0) {
self.init(red: CGFloat((hex>>16)&0xFF)/255.0, green: CGFloat((hex>>8)&0xFF)/255.0, blue: CGFloat((hex)&0xFF)/255.0, alpha: CGFloat(255 * alpha) / 255)
}
convenience init(hexString: String, alpha: Double = 1.0) {
let hex = hexString.trimmingCharacters(in: CharacterSet.alphanumerics.inverted)
var int = UInt32()
Scanner(string: hex).scanHexInt32(&int)
let r, g, b: UInt32
switch hex.count {
case 3: // RGB (12-bit)
(r, g, b) = ((int >> 8) * 17, (int >> 4 & 0xF) * 17, (int & 0xF) * 17)
case 6: // RGB (24-bit)
(r, g, b) = (int >> 16, int >> 8 & 0xFF, int & 0xFF)
default:
(r, g, b) = (1, 1, 0)
}
self.init(red: CGFloat(r) / 255, green: CGFloat(g) / 255, blue: CGFloat(b) / 255, alpha: CGFloat(255 * alpha) / 255)
}
}
utilisez-les comme ci-dessous:
Vieille Réponse
j'ai fait un autre UIColor extension dans Swift 2.2, il peut utiliser la valeur hex à UIColor droit, souhaiter peut aider quelqu'un:
extension UIColor {
convenience init(hex: Int, alpha: Double = 1.0) {
self.init(red: CGFloat((hex>>16)&0xFF)/255.0, green:CGFloat((hex>>8)&0xFF)/255.0, blue: CGFloat((hex)&0xFF)/255.0, alpha: CGFloat(255 * alpha) / 255)
}
}
et l'utiliser comme ceci:
UIColor(hex: 0xffffff) // r 1.0 g 1.0 b 1.0 a 1.0
UIColor(hex: 0xffffff, alpha: 0.5) // r 1.0 g 1.0 b 1.0 a 0.5
voici une extension Swift sur UIColor qui prend une chaîne hex:
import UIKit
extension UIColor {
convenience init(hexString: String) {
// Trim leading '#' if needed
var cleanedHexString = hexString
if hexString.hasPrefix("#") {
// cleanedHexString = dropFirst(hexString) // Swift 1.2
cleanedHexString = String(hexString.characters.dropFirst()) // Swift 2
}
// String -> UInt32
var rgbValue: UInt32 = 0
NSScanner(string: cleanedHexString).scanHexInt(&rgbValue)
// UInt32 -> R,G,B
let red = CGFloat((rgbValue >> 16) & 0xff) / 255.0
let green = CGFloat((rgbValue >> 08) & 0xff) / 255.0
let blue = CGFloat((rgbValue >> 00) & 0xff) / 255.0
self.init(red: red, green: green, blue: blue, alpha: 1.0)
}
}
public static func hexStringToUIColor (hex:String) -> UIColor {
var cString:String = hex.trimmingCharacters(in: .whitespacesAndNewlines).uppercased()
if (cString.hasPrefix("#")) {
cString.remove(at: cString.startIndex)
}
if ((cString.characters.count) == 6) {
var rgbValue:UInt32 = 0
Scanner(string: cString).scanHexInt32(&rgbValue)
return UIColor(
red: CGFloat((rgbValue & 0xFF0000) >> 16) / 255.0,
green: CGFloat((rgbValue & 0x00FF00) >> 8) / 255.0,
blue: CGFloat(rgbValue & 0x0000FF) / 255.0,
alpha: CGFloat(1.0)
)
}else if ((cString.characters.count) == 8) {
var rgbValue:UInt32 = 0
Scanner(string: cString).scanHexInt32(&rgbValue)
return UIColor(
red: CGFloat((rgbValue & 0x00FF0000) >> 16) / 255.0,
green: CGFloat((rgbValue & 0x0000FF00) >> 8) / 255.0,
blue: CGFloat(rgbValue & 0x000000FF) / 255.0,
alpha: CGFloat((rgbValue & 0xFF000000) >> 24) / 255.0
)
}else{
return UIColor.gray
}
}
comment utiliser
var color: UIColor = hexStringToUIColor(hex: "#00ff00"); // Without transparency
var colorWithTransparency: UIColor = hexStringToUIColor(hex: "#dd00ff00"); // With transparency
j'ai fusionné quelques idées de ce fil de réponses et l'ai mis à jour à Swift 4 .
extension UIColor {
convenience init(hex: String, alpha: CGFloat = 1.0) {
var cString:String = hex.trimmingCharacters(in: .whitespacesAndNewlines).uppercased()
if (cString.hasPrefix("#")) { cString.removeFirst() }
if ((cString.count) != 6) {
self.init(hex: "ff0000") // return red color for wrong hex input
return
}
var rgbValue: UInt32 = 0
Scanner(string: cString).scanHexInt32(&rgbValue)
self.init(red: CGFloat((rgbValue & 0xFF0000) >> 16) / 255.0,
green: CGFloat((rgbValue & 0x00FF00) >> 8) / 255.0,
blue: CGFloat(rgbValue & 0x0000FF) / 255.0,
alpha: alpha)
}
}
, Vous pouvez alors l'utiliser comme ceci:
UIColor(hex: "#ff0000") // with #
UIColor(hex: "ff0000") // without #
UIColor(hex: "ff0000", alpha: 0.5) // using optional alpha value
la version Swift 4 ressemble à ceci:
extension UIColor {
convenience init(hexString: String, alpha: CGFloat = 1.0) {
let hexString: String = hexString.trimmingCharacters(in: CharacterSet.whitespacesAndNewlines)
let scanner = Scanner(string: hexString)
if (hexString.hasPrefix("#")) {
scanner.scanLocation = 1
}
var color: UInt32 = 0
scanner.scanHexInt32(&color)
let mask = 0x000000FF
let r = Int(color >> 16) & mask
let g = Int(color >> 8) & mask
let b = Int(color) & mask
let red = CGFloat(r) / 255.0
let green = CGFloat(g) / 255.0
let blue = CGFloat(b) / 255.0
self.init(red:red, green:green, blue:blue, alpha:alpha)
}
func toHexString() -> String {
var r:CGFloat = 0
var g:CGFloat = 0
var b:CGFloat = 0
var a:CGFloat = 0
getRed(&r, green: &g, blue: &b, alpha: &a)
let rgb:Int = (Int)(r*255)<<16 | (Int)(g*255)<<8 | (Int)(b*255)<<0
return String(format:"#%06x", rgb)
}
}
Supportant 7 couleur Hexadécimale types
il y a 7 formats de couleurs hexadécimales: ""# FF0000"," 0xFF0000"," FF0000"," F00"," rouge", 0x00FF00, 16711935
NSColorParser.nsColor("#FF0000",1)//red nsColor
NSColorParser.nsColor("FF0",1)//red nsColor
NSColorParser.nsColor("0xFF0000",1)//red nsColor
NSColorParser.nsColor("#FF0000",1)//red nsColor
NSColorParser.nsColor("FF0000",1)//red nsColor
NSColorParser.nsColor(0xFF0000,1)//red nsColor
NSColorParser.nsColor(16711935,1)//red nsColor
attention: ce n'est pas une" solution à un seul fichier", il y a quelques dépendances, mais les traquer peut-être plus rapidement que d'effectuer des recherches À partir de zéro.
Permalink:
https://github.com/eonist/Element/wiki/Progress#supporting-7-hex-color-types
Swift 2.0
le code ci-dessous est testé sur xcode 7.2
import UIKit
extension UIColor{
public convenience init?(colorCodeInHex: String, alpha: Float = 1.0){
var filterColorCode:String = colorCodeInHex.stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString("#", withString: "")
if filterColorCode.characters.count != 6 {
self.init(red: 0.0, green: 0.0, blue: 0.0, alpha: CGFloat(alpha))
return
}
filterColorCode = filterColorCode.stringByTrimmingCharactersInSet(NSCharacterSet.whitespaceAndNewlineCharacterSet()).uppercaseString
var range = Range(start: filterColorCode.startIndex.advancedBy(0), end: filterColorCode.startIndex.advancedBy(2))
let rString = filterColorCode.substringWithRange(range)
range = Range(start: filterColorCode.startIndex.advancedBy(2), end: filterColorCode.startIndex.advancedBy(4))
let gString = filterColorCode.substringWithRange(range)
range = Range(start: filterColorCode.startIndex.advancedBy(4), end: filterColorCode.startIndex.advancedBy(6))
let bString = filterColorCode.substringWithRange(range)
var r:CUnsignedInt = 0, g:CUnsignedInt = 0, b:CUnsignedInt = 0;
NSScanner(string: rString).scanHexInt(&r)
NSScanner(string: gString).scanHexInt(&g)
NSScanner(string: bString).scanHexInt(&b)
self.init(red: CGFloat(r) / 255.0, green: CGFloat(g) / 255.0, blue: CGFloat(b) / 255.0, alpha: CGFloat(alpha))
return
}
}
Swift 2.0:
faire une extension de UIColor.
extension UIColor {
convenience init(hexString:String) {
let hexString:NSString = hexString.stringByTrimmingCharactersInSet(NSCharacterSet.whitespaceAndNewlineCharacterSet())
let scanner = NSScanner(string: hexString as String)
if (hexString.hasPrefix("#")) {
scanner.scanLocation = 1
}
var color:UInt32 = 0
scanner.scanHexInt(&color)
let mask = 0x000000FF
let r = Int(color >> 16) & mask
let g = Int(color >> 8) & mask
let b = Int(color) & mask
let red = CGFloat(r) / 255.0
let green = CGFloat(g) / 255.0
let blue = CGFloat(b) / 255.0
self.init(red:red, green:green, blue:blue, alpha:1)
}
func toHexString() -> String {
var r:CGFloat = 0
var g:CGFloat = 0
var b:CGFloat = 0
var a:CGFloat = 0
getRed(&r, green: &g, blue: &b, alpha: &a)
let rgb:Int = (Int)(r*255)<<16 | (Int)(g*255)<<8 | (Int)(b*255)<<0
return NSString(format:"#%06x", rgb) as String
}
}
Utilisation:
//Hex to Color
let countPartColor = UIColor(hexString: "E43038")
//Color to Hex
let colorHexString = UIColor(red: 228, green: 48, blue: 56, alpha: 1.0).toHexString()
Swift 2.0:
Dans le viewDidLoad()
var viewColor:UIColor
viewColor = UIColor()
let colorInt:UInt
colorInt = 0x000000
viewColor = UIColorFromRGB(colorInt)
self.View.backgroundColor=viewColor
func UIColorFromRGB(rgbValue: UInt) -> UIColor {
return UIColor(
red: CGFloat((rgbValue & 0xFF0000) >> 16) / 255.0,
green: CGFloat((rgbValue & 0x00FF00) >> 8) / 255.0,
blue: CGFloat(rgbValue & 0x0000FF) / 255.0,
alpha: CGFloat(1.0)
)
}
pour swift 3
extension String {
var hexColor: UIColor {
let hex = trimmingCharacters(in: CharacterSet.alphanumerics.inverted)
var int = UInt32()
Scanner(string: hex).scanHexInt32(&int)
let a, r, g, b: UInt32
switch hex.characters.count {
case 3: // RGB (12-bit)
(a, r, g, b) = (255, (int >> 8) * 17, (int >> 4 & 0xF) * 17, (int & 0xF) * 17)
case 6: // RGB (24-bit)
(a, r, g, b) = (255, int >> 16, int >> 8 & 0xFF, int & 0xFF)
case 8: // ARGB (32-bit)
(a, r, g, b) = (int >> 24, int >> 16 & 0xFF, int >> 8 & 0xFF, int & 0xFF)
default:
return .clear
}
return UIColor(red: CGFloat(r) / 255, green: CGFloat(g) / 255, blue: CGFloat(b) / 255, alpha: CGFloat(a) / 255)
}
}
vous pouvez utiliser cette extension sur UIColor qui convertit votre chaîne (hexadécimal , RGBA) en UIColor et vice versa.
extension UIColor {
//Convert RGBA String to UIColor object
//"rgbaString" must be separated by space "0.5 0.6 0.7 1.0" 50% of Red 60% of Green 70% of Blue Alpha 100%
public convenience init?(rgbaString : String){
self.init(ciColor: CIColor(string: rgbaString))
}
//Convert UIColor to RGBA String
func toRGBAString()-> String {
var r: CGFloat = 0
var g: CGFloat = 0
var b: CGFloat = 0
var a: CGFloat = 0
self.getRed(&r, green: &g, blue: &b, alpha: &a)
return "\(r) \(g) \(b) \(a)"
}
//return UIColor from Hexadecimal Color string
public convenience init?(hexString: String) {
let r, g, b, a: CGFloat
if hexString.hasPrefix("#") {
let start = hexString.index(hexString.startIndex, offsetBy: 1)
let hexColor = hexString.substring(from: start)
if hexColor.characters.count == 8 {
let scanner = Scanner(string: hexColor)
var hexNumber: UInt64 = 0
if scanner.scanHexInt64(&hexNumber) {
r = CGFloat((hexNumber & 0xff000000) >> 24) / 255
g = CGFloat((hexNumber & 0x00ff0000) >> 16) / 255
b = CGFloat((hexNumber & 0x0000ff00) >> 8) / 255
a = CGFloat(hexNumber & 0x000000ff) / 255
self.init(red: r, green: g, blue: b, alpha: a)
return
}
}
}
return nil
}
// Convert UIColor to Hexadecimal String
func toHexString() -> String {
var r: CGFloat = 0
var g: CGFloat = 0
var b: CGFloat = 0
var a: CGFloat = 0
self.getRed(&r, green: &g, blue: &b, alpha: &a)
return String(
format: "%02X%02X%02X",
Int(r * 0xff),
Int(g * 0xff),
Int(b * 0xff))
}
}
UIColor extension, cela vous aidera grandement! (version: Swift 4.0 )
import UIKit
extension UIColor {
/// rgb颜色
convenience init(r: CGFloat, g: CGFloat, b: CGFloat) {
self.init(red: r/255.0 ,green: g/255.0 ,blue: b/255.0 ,alpha:1.0)
}
/// 纯色(用于灰色)
convenience init(gray: CGFloat) {
self.init(red: gray/255.0 ,green: gray/255.0 ,blue: gray/255.0 ,alpha:1.0)
}
/// 随机色
class func randomCGColor() -> UIColor {
return UIColor(r: CGFloat(arc4random_uniform(256)), g: CGFloat(arc4random_uniform(256)), b: CGFloat(arc4random_uniform(256)))
}
/// hex颜色-Int
convenience init(hex:Int, alpha:CGFloat = 1.0) {
self.init(
red: CGFloat((hex & 0xFF0000) >> 16) / 255.0,
green: CGFloat((hex & 0x00FF00) >> 8) / 255.0,
blue: CGFloat((hex & 0x0000FF) >> 0) / 255.0,
alpha: alpha
)
}
/// hex颜色-String
convenience init(hexString: String){
var red: CGFloat = 0.0
var green: CGFloat = 0.0
var blue: CGFloat = 0.0
var alpha: CGFloat = 1.0
let scanner = Scanner(string: hexString)
var hexValue: CUnsignedLongLong = 0
if scanner.scanHexInt64(&hexValue) {
switch (hexString.characters.count) {
case 3:
red = CGFloat((hexValue & 0xF00) >> 8) / 15.0
green = CGFloat((hexValue & 0x0F0) >> 4) / 15.0
blue = CGFloat(hexValue & 0x00F) / 15.0
case 4:
red = CGFloat((hexValue & 0xF000) >> 12) / 15.0
green = CGFloat((hexValue & 0x0F00) >> 8) / 15.0
blue = CGFloat((hexValue & 0x00F0) >> 4) / 15.0
alpha = CGFloat(hexValue & 0x000F) / 15.0
case 6:
red = CGFloat((hexValue & 0xFF0000) >> 16) / 255.0
green = CGFloat((hexValue & 0x00FF00) >> 8) / 255.0
blue = CGFloat(hexValue & 0x0000FF) / 255.0
case 8:
alpha = CGFloat((hexValue & 0xFF000000) >> 24) / 255.0
red = CGFloat((hexValue & 0x00FF0000) >> 16) / 255.0
green = CGFloat((hexValue & 0x0000FF00) >> 8) / 255.0
blue = CGFloat(hexValue & 0x000000FF) / 255.0
default:
log.info("Invalid RGB string, number of characters after '#' should be either 3, 4, 6 or 8")
}
} else {
log.error("Scan hex error")
}
self.init(red:red, green:green, blue:blue, alpha:alpha)
}}
RGBA version Swift 3/4
j'aime la réponse de @Luca car je pense qu'elle est la plus élégante.
Toutefois je ne veux pas que mes couleurs spécifié dans ARGB . Je préférerais RGBA + j'ai aussi eu besoin de pirater dans le cas de traiter avec des chaînes qui spécifient un caractère pour chacun des canaux " #FFFA ".
This la version ajoute aussi le lancer d'erreur + supprime le caractère ' # ' s'il est inclus dans la chaîne. Voici mon formulaire modifié pour Swift.
public enum ColourParsingError: Error
{
case invalidInput(String)
}
extension UIColor {
public convenience init(hexString: String) throws
{
let hexString = hexString.replacingOccurrences(of: "#", with: "")
let hex = hexString.trimmingCharacters(in:NSCharacterSet.alphanumerics.inverted)
var int = UInt32()
Scanner(string: hex).scanHexInt32(&int)
let a, r, g, b: UInt32
switch hex.count
{
case 3: // RGB (12-bit)
(r, g, b,a) = ((int >> 8) * 17, (int >> 4 & 0xF) * 17, (int & 0xF) * 17,255)
//iCSS specification in the form of #F0FA
case 4: // RGB (24-bit)
(r, g, b,a) = ((int >> 12) * 17, (int >> 8 & 0xF) * 17, (int >> 4 & 0xF) * 17, (int & 0xF) * 17)
case 6: // RGB (24-bit)
(r, g, b, a) = (int >> 16, int >> 8 & 0xFF, int & 0xFF,255)
case 8: // ARGB (32-bit)
(r, g, b, a) = (int >> 24, int >> 16 & 0xFF, int >> 8 & 0xFF, int & 0xFF)
default:
throw ColourParsingError.invalidInput("String is not a valid hex colour string: \(hexString)")
}
self.init(red: CGFloat(r) / 255, green: CGFloat(g) / 255, blue: CGFloat(b) / 255, alpha: CGFloat(a) / 255)
}
}
juste un ajout à la première réponse
(n'ont pas cehcked l'alpha, mai besoin d'ajouter un if netHext > 0xffffff ):
extension UIColor {
struct COLORS_HEX {
static let Primary = 0xffffff
static let PrimaryDark = 0x000000
static let Accent = 0xe89549
static let AccentDark = 0xe27b2a
static let TextWhiteSemiTransparent = 0x80ffffff
}
convenience init(red: Int, green: Int, blue: Int, alphaH: Int) {
assert(red >= 0 && red <= 255, "Invalid red component")
assert(green >= 0 && green <= 255, "Invalid green component")
assert(blue >= 0 && blue <= 255, "Invalid blue component")
assert(alphaH >= 0 && alphaH <= 255, "Invalid alpha component")
self.init(red: CGFloat(red) / 255.0, green: CGFloat(green) / 255.0, blue: CGFloat(blue) / 255.0, alpha: CGFloat(alphaH) / 255.0)
}
convenience init(netHex:Int) {
self.init(red:(netHex >> 16) & 0xff, green:(netHex >> 8) & 0xff, blue:netHex & 0xff, alphaH: (netHex >> 24) & 0xff)
}
}
Swift 2.3: Extension UIColor. Je Pense que c'est plus simple.
extension UIColor {
static func colorFromHex(hexString: String, alpha: CGFloat = 1) -> UIColor {
//checking if hex has 7 characters or not including '#'
if hexString.characters.count < 7 {
return UIColor.whiteColor()
}
//string by removing hash
let hexStringWithoutHash = hexString.substringFromIndex(hexString.startIndex.advancedBy(1))
//I am extracting three parts of hex color Red (first 2 characters), Green (middle 2 characters), Blue (last two characters)
let eachColor = [
hexStringWithoutHash.substringWithRange(hexStringWithoutHash.startIndex...hexStringWithoutHash.startIndex.advancedBy(1)),
hexStringWithoutHash.substringWithRange(hexStringWithoutHash.startIndex.advancedBy(2)...hexStringWithoutHash.startIndex.advancedBy(3)),
hexStringWithoutHash.substringWithRange(hexStringWithoutHash.startIndex.advancedBy(4)...hexStringWithoutHash.startIndex.advancedBy(5))]
let hexForEach = eachColor.map {CGFloat(Int("151900920", radix: 16) ?? 0)} //radix is base of numeric system you want to convert to, Hexadecimal has base 16
//return the color by making color
return UIColor(red: hexForEach[0] / 255, green: hexForEach[1] / 255, blue: hexForEach[2] / 255, alpha: alpha)
}
}
Utilisation:
let color = UIColor.colorFromHex("#25ac09")
Swift 3
extension UIColor {
convenience init(r: Int, g: Int, b: Int, a: Int = 255) {
self.init(red: CGFloat(r) / 255.0, green: CGFloat(g) / 255.0, blue: CGFloat(b) / 255.0, alpha: CGFloat(a) / 255.0)
}
convenience init(netHex:Int) {
self.init(r:(netHex >> 16) & 0xff, g:(netHex >> 8) & 0xff, b:netHex & 0xff)
}
}
utilisant:
self.view.backgroundColor = UIColor(netHex: 0x27ae60)
Swift 4.0
utilisez cette seule ligne de méthode
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
let color = UIColor(hexColor: "FF00A0")
self.view.backgroundColor = color
}
vous devez créer une nouvelle classe ou utiliser n'importe quel contrôleur où vous avez besoin d'utiliser la couleur Hex. Cette classe d'extension vous fournit UIColor qui convertira Hex en couleur RGB.
extension UIColor {
convenience init(hexColor: String) {
let scannHex = Scanner(string: hexColor)
var rgbValue: UInt64 = 0
scannHex.scanLocation = 0
scannHex.scanHexInt64(&rgbValue)
let r = (rgbValue & 0xff0000) >> 16
let g = (rgbValue & 0xff00) >> 8
let b = rgbValue & 0xff
self.init(
red: CGFloat(r) / 0xff,
green: CGFloat(g) / 0xff,
blue: CGFloat(b) / 0xff, alpha: 1
)
}
}
extension UIColor {
convenience init(hex: Int, alpha: Double = 1.0) {
self.init(red: CGFloat((hex>>16)&0xFF)/255.0, green:CGFloat((hex>>8)&0xFF)/255.0, blue: CGFloat((hex)&0xFF)/255.0, alpha: CGFloat(255 * alpha) / 255)
}
}
utiliser cette extension comme:
let selectedColor = UIColor(hex: 0xFFFFFF)
let selectedColor = UIColor(hex: 0xFFFFFF, alpha: 0.5)
j'ai créé une petite fonction,je l'ai placée d'où je peux l'utiliser globalement et travailler très bien avec swift 2.1:
func getColorFromHex(rgbValue:UInt32)->UIColor{
let red = CGFloat((rgbValue & 0xFF0000) >> 16)/255.0
let green = CGFloat((rgbValue & 0xFF00) >> 8)/255.0
let blue = CGFloat(rgbValue & 0xFF)/255.0
return UIColor(red:red, green:green, blue:blue, alpha:1.0)
}
utilisation:
getColorFromHex(0xffffff)