Comment tracer la courbe de ROC en Python
j'essaie de tracer une courbe ROC pour évaluer la précision d'un modèle de prédiction que j'ai développé en Python en utilisant des paquets de régression logistique. J'ai calculé le taux de vrai positif ainsi que le taux de faux positifs; cependant, je suis incapable de comprendre comment les repérer correctement à l'aide de matplotlib et calculer la valeur de la SSC. Comment pourrais-je le faire?
8 réponses
voici deux façons d'essayer:
# calculate the fpr and tpr for all thresholds of the classification
probs = model.predict_proba(X_test)
preds = probs[:,1]
fpr, tpr, threshold = metrics.roc_curve(y_test, preds)
roc_auc = metrics.auc(fpr, tpr)
# method I: plt
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.title('Receiver Operating Characteristic')
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, 'b', label = 'AUC = %0.2f' % roc_auc)
plt.legend(loc = 'lower right')
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1],'r--')
plt.xlim([0, 1])
plt.ylim([0, 1])
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.show()
# method II: ggplot
from ggplot import *
df = pd.DataFrame(dict(fpr = fpr, tpr = tpr))
ggplot(df, aes(x = 'fpr', y = 'tpr')) + geom_line() + geom_abline(linetype = 'dashed')
ou essayer
ggplot(df, aes(x = 'fpr', ymin = 0, ymax = 'tpr')) + geom_line(aes(y = 'tpr')) + geom_area(alpha = 0.2) + ggtitle("ROC Curve w/ AUC = %s" % str(roc_auc))
ce n'est pas du tout clair ce que le problème est ici, mais si vous avez un tableau true_positive_rate et un tableau false_positive_rate, puis tracer la courbe ROC et obtenir L'AUC est aussi simple que:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = # false_positive_rate
y = # true_positive_rate
# This is the ROC curve
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.show()
# This is the AUC
auc = np.trapz(y,x)
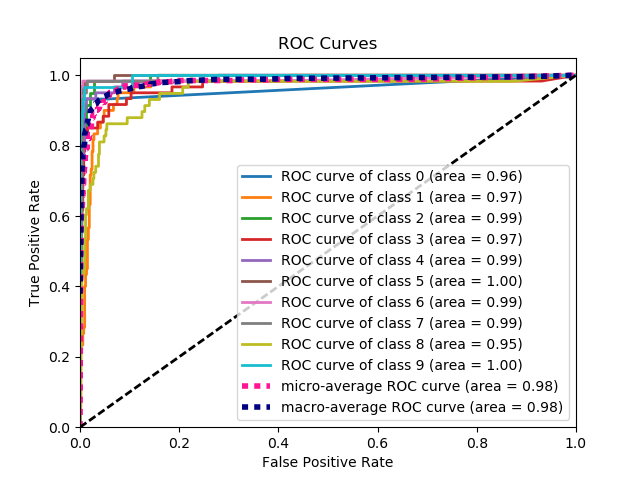
C'est la façon la plus simple de tracer une courbe ROC, étant donné un ensemble d'étiquettes de vérité de terrain et de probabilités prédites. La meilleure partie est, il trace la courbe de ROC pour toutes les classes, de sorte que vous obtenez plusieurs courbes d'apparence soignée ainsi
import scikitplot as skplt
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
y_true = # ground truth labels
y_probas = # predicted probabilities generated by sklearn classifier
skplt.metrics.plot_roc_curve(y_true, y_probas)
plt.show()
voici une courbe d'échantillon générée par plot_roc_curve. J'ai utilisé l'ensemble de données sample digits de scikit-learn pour qu'il y ait 10 classes. Notez qu'une courbe ROC est tracée pour chaque classe.
Avertissement: veuillez Noter que cela utilise le scitkit-plot bibliothèque, que j'ai construit.
Voici un code python :
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
score = np.array([0.9, 0.8, 0.7, 0.6, 0.55, 0.54, 0.53, 0.52, 0.51, 0.505, 0.4, 0.39, 0.38, 0.37, 0.36, 0.35, 0.34, 0.33, 0.30, 0.1])
y = np.array([1,1,0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1,0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1 , 0, 1, 0])
roc_x = []
roc_y = []
min_score = min(score)
max_score = max(score)
thr = np.linspace(min_score, max_score, 30)
FP=0
TP=0
N = sum(y)
P = len(y) - N
for (i, T) in enumerate(thr):
for i in range(0, len(score)):
if (score[i] > T):
if (y[i]==1):
TP = TP + 1
if (y[i]==0):
FP = FP + 1
roc_x.append(FP/float(N))
roc_y.append(TP/float(P))
FP=0
TP=0
plt.scatter(roc_x, roc_y)
plt.show()
Plus référence
courbe de L'ASC pour la Classification binaire à l'aide de matplotlib
from sklearn import svm, datasets
from sklearn import metrics
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Load Breast Cancer Data Set
breast_cancer = load_breast_cancer()
X = breast_cancer.data
y = breast_cancer.target
Diviser le jeu de données
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.33, random_state=44)
Modèle
clf = LogisticRegression(penalty='l2', C=0.1)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
Précision
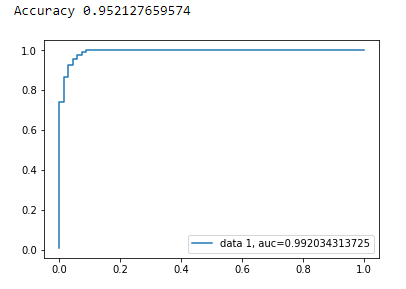
print("Accuracy", metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
courbe de l ' ASC
y_pred_proba = clf.predict_proba(X_test)[::,1]
fpr, tpr, _ = metrics.roc_curve(y_test, y_pred_proba)
auc = metrics.roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred_proba)
plt.plot(fpr,tpr,label="data 1, auc="+str(auc))
plt.legend(loc=4)
plt.show()
les réponses précédentes supposent que vous avez bien calculé vous-même TP/Sens. C'est une mauvaise idée de faire cela manuellement, il est facile de faire des erreurs avec les calculs, plutôt utiliser une fonction de bibliothèque pour tout cela.
la fonction plot_roc dans scikit_lean fait exactement ce dont vous avez besoin: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/model_selection/plot_roc.html
la partie essentielle du code est:
for i in range(n_classes):
fpr[i], tpr[i], _ = roc_curve(y_test[:, i], y_score[:, i])
roc_auc[i] = auc(fpr[i], tpr[i])
j'ai fait une fonction simple incluse dans un paquet pour la courbe ROC. Je viens de commencer à pratiquer l'apprentissage machine donc s'il vous plaît aussi me faire savoir si ce code a un problème!
consultez le fichier readme de github pour plus de détails! :)
https://github.com/bc123456/ROC
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, accuracy_score, roc_auc_score, roc_curve
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import numpy as np
def plot_ROC(y_train_true, y_train_prob, y_test_true, y_test_prob):
'''
a funciton to plot the ROC curve for train labels and test labels.
Use the best threshold found in train set to classify items in test set.
'''
fpr_train, tpr_train, thresholds_train = roc_curve(y_train_true, y_train_prob, pos_label =True)
sum_sensitivity_specificity_train = tpr_train + (1-fpr_train)
best_threshold_id_train = np.argmax(sum_sensitivity_specificity_train)
best_threshold = thresholds_train[best_threshold_id_train]
best_fpr_train = fpr_train[best_threshold_id_train]
best_tpr_train = tpr_train[best_threshold_id_train]
y_train = y_train_prob > best_threshold
cm_train = confusion_matrix(y_train_true, y_train)
acc_train = accuracy_score(y_train_true, y_train)
auc_train = roc_auc_score(y_train_true, y_train)
print 'Train Accuracy: %s ' %acc_train
print 'Train AUC: %s ' %auc_train
print 'Train Confusion Matrix:'
print cm_train
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
ax = fig.add_subplot(121)
curve1 = ax.plot(fpr_train, tpr_train)
curve2 = ax.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='navy', linestyle='--')
dot = ax.plot(best_fpr_train, best_tpr_train, marker='o', color='black')
ax.text(best_fpr_train, best_tpr_train, s = '(%.3f,%.3f)' %(best_fpr_train, best_tpr_train))
plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
plt.title('ROC curve (Train), AUC = %.4f'%auc_train)
fpr_test, tpr_test, thresholds_test = roc_curve(y_test_true, y_test_prob, pos_label =True)
y_test = y_test_prob > best_threshold
cm_test = confusion_matrix(y_test_true, y_test)
acc_test = accuracy_score(y_test_true, y_test)
auc_test = roc_auc_score(y_test_true, y_test)
print 'Test Accuracy: %s ' %acc_test
print 'Test AUC: %s ' %auc_test
print 'Test Confusion Matrix:'
print cm_test
tpr_score = float(cm_test[1][1])/(cm_test[1][1] + cm_test[1][0])
fpr_score = float(cm_test[0][1])/(cm_test[0][0]+ cm_test[0][1])
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122)
curve1 = ax2.plot(fpr_test, tpr_test)
curve2 = ax2.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='navy', linestyle='--')
dot = ax2.plot(fpr_score, tpr_score, marker='o', color='black')
ax2.text(fpr_score, tpr_score, s = '(%.3f,%.3f)' %(fpr_score, tpr_score))
plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
plt.title('ROC curve (Test), AUC = %.4f'%auc_test)
plt.savefig('ROC', dpi = 500)
plt.show()
return best_threshold
from sklearn import metrics
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
y_true = # true labels
y_probas = # predicted results
fpr, tpr, thresholds = metrics.roc_curve(y_true, y_probas, pos_label=0)
# Print ROC curve
plt.plot(fpr,tpr)
plt.show()
# Print AUC
auc = np.trapz(tpr,fpr)
print('AUC:', auc)